Façade Pattern
Description:
» The role of the Façade pattern is to provide different high-level views of subsystems whose details are hidden from users;» The Façade pattern is used to reorganize a system with many subsystems into identifiable layers with single entry points; essentially, simplifies the interface to a complex subsystem;
» The Façade pattern can be used to make frequent use of a system faster or to differentiate between novices and power users;
» Everything in the façade has to be public so that the Client, which is compiled into a different assembly, can access it; all the classes have the default internal visibility, limiting access to them to the assembly in which they were compiled (excluding the Client);
» The Façade pattern uses the C# concept of namespaces.
Alternative implementations of the Façade pattern
Transparent Façades:
» Change all the internal modifiers to public, which will make the façade optional, or transparent;
» That is, as well as being able to go through the Façade, the client will be able to instantiate System classes directly.
Static Façades:
» This implies that façade is a static class;
» No instantiation is necessary; the user interfaces with the façade class directly.
Use When:
» Subsystem operations can only be called through the Façade;» Subsystem operations can be called directly as well as through the Façade.
//Define the Façade Object.
//Define the Facade class which provides a common view into the defined high-level systems (objects).
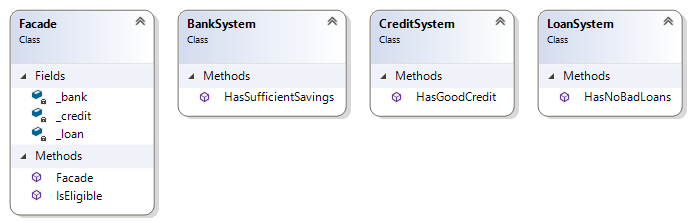
public class Facade
{
private BankSystem _bank;
private LoanSystem _loan;
private CreditSystem _credit;
public Facade()
{
_bank = new BankSystem();
_loan = new LoanSystem();
_credit = new CreditSystem();
}
//The IsEligible() method will invoke separate methods in each individual object and return a single response.
public bool IsEligible(string customerId, int amount)
{
bool eligible = true;
Console.WriteLine("Customer {0} applies for {1:C} loan\n", customerId, amount);
if (!_bank.HasSufficientSavings(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_loan.HasNoBadLoans(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_credit.HasGoodCredit(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
return eligible;
}
}
//Define the Facade class which provides a common view into the defined high-level systems (objects).
public class Facade
{
private BankSystem _bank;
private LoanSystem _loan;
private CreditSystem _credit;
public Facade()
{
_bank = new BankSystem();
_loan = new LoanSystem();
_credit = new CreditSystem();
}
//The IsEligible() method will invoke separate methods in each individual object and return a single response.
public bool IsEligible(string customerId, int amount)
{
bool eligible = true;
Console.WriteLine("Customer {0} applies for {1:C} loan\n", customerId, amount);
if (!_bank.HasSufficientSavings(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_loan.HasNoBadLoans(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_credit.HasGoodCredit(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
return eligible;
}
}
//Define the Façade Object.
//Define the Facade class which provides a common view into the defined high-level systems (objects).
public class Facade
{
private BankSystem _bank;
private LoanSystem _loan;
private CreditSystem _credit;
public Facade()
{
_bank = new BankSystem();
_loan = new LoanSystem();
_credit = new CreditSystem();
}
//The IsEligible() method will invoke separate methods in each individual object and return a single response.
public bool IsEligible(string customerId, int amount)
{
bool eligible = true;
Console.WriteLine("Customer {0} applies for {1:C} loan\n", customerId, amount);
if (!_bank.HasSufficientSavings(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_loan.HasNoBadLoans(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_credit.HasGoodCredit(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
return eligible;
}
}
//Define the Facade class which provides a common view into the defined high-level systems (objects).
public class Facade
{
private BankSystem _bank;
private LoanSystem _loan;
private CreditSystem _credit;
public Facade()
{
_bank = new BankSystem();
_loan = new LoanSystem();
_credit = new CreditSystem();
}
//The IsEligible() method will invoke separate methods in each individual object and return a single response.
public bool IsEligible(string customerId, int amount)
{
bool eligible = true;
Console.WriteLine("Customer {0} applies for {1:C} loan\n", customerId, amount);
if (!_bank.HasSufficientSavings(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_loan.HasNoBadLoans(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
else if (!_credit.HasGoodCredit(customerId))
{
eligible = false;
}
return eligible;
}
}