Prototype Pattern
Description:
» The Prototype pattern is used to create new objects by cloning one of a few stored prototypes;» The Prototype pattern ensures that when copies of complex objects are made, they are true copies;
» Given a key, the program creates an object of the required type, not by instantiation, but by copying a clean instance of the class. The copies, or clones, are objects in their own right, and the intention of the pattern is that their state can be altered at will without affecting the prototype;
» Designs that make heavy use of the Composite and Decorator patterns often can benefit from the Prototype pattern as well;
» Prototypes are useful when object initialization is expensive and you anticipate few variations on the initialization parameters.
Use When:
» Hide concrete classes from the client;» Add and remove new classes (via prototypes) at runtime;
» Keep the number of classes in the system to a minimum;
» Adapt to changing structures of data at runtime.
//Define the Prototype Interface and Handler Objects.
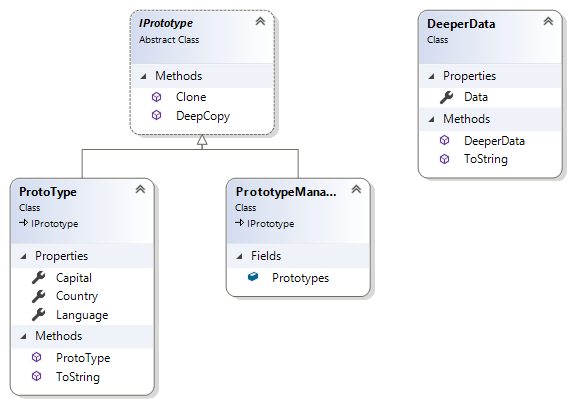
//Define the IPrototype abstract to be used as the base class for the main Prototype classes.
//The class defines the Clone() method (which does a shallow copy of the original object) and the DeepCopy() method.
//A shallow copy creates a new instance of the same type as the original object, and then copies the nonstatic fields of the original object; if the field is a value type, a bit-by-bit copy of the field is performed; If the field is a reference type, the reference is copied but the referred object is not; therefore, the reference in the original object and the reference in the clone point to the same object.
//In contrast, a deep copy of an object duplicates everything directly or indirectly referenced by the fields in the object.
[Serializable]
public abstract class IPrototype
{
public ProtoType Clone()
{
return (ProtoType) MemberwiseClone();
}
public ProtoType DeepCopy()
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
ProtoType copy = (ProtoType) formatter.Deserialize(stream);
stream.Close();
return (copy);
}
}
//The DeeperData class (object) is an extension to the Prototype class (object) and represents a referred object in the Prototype class (object).
[Serializable]
public class DeeperData
{
public string Data { get; set; }
public DeeperData(string s)
{
Data = s;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return (Data);
}
}
//The ProtoType class (object) represents the original prototype class, from which other classes will be cloned.
[Serializable]
public class ProtoType : IPrototype
{
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Capital { get; set; }
public DeeperData Language { get; set; }
public ProtoType(string country, string capital, string language)
{
Country = country;
Capital = capital;
Language = new DeeperData(language);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}\t\t{1}\t\t->{2}", Country, Capital, Language);
}
}
//Define the IPrototype abstract to be used as the base class for the main Prototype classes.
//The class defines the Clone() method (which does a shallow copy of the original object) and the DeepCopy() method.
//A shallow copy creates a new instance of the same type as the original object, and then copies the nonstatic fields of the original object; if the field is a value type, a bit-by-bit copy of the field is performed; If the field is a reference type, the reference is copied but the referred object is not; therefore, the reference in the original object and the reference in the clone point to the same object.
//In contrast, a deep copy of an object duplicates everything directly or indirectly referenced by the fields in the object.
[Serializable]
public abstract class IPrototype
{
public ProtoType Clone()
{
return (ProtoType) MemberwiseClone();
}
public ProtoType DeepCopy()
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
ProtoType copy = (ProtoType) formatter.Deserialize(stream);
stream.Close();
return (copy);
}
}
//The DeeperData class (object) is an extension to the Prototype class (object) and represents a referred object in the Prototype class (object).
[Serializable]
public class DeeperData
{
public string Data { get; set; }
public DeeperData(string s)
{
Data = s;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return (Data);
}
}
//The ProtoType class (object) represents the original prototype class, from which other classes will be cloned.
[Serializable]
public class ProtoType : IPrototype
{
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Capital { get; set; }
public DeeperData Language { get; set; }
public ProtoType(string country, string capital, string language)
{
Country = country;
Capital = capital;
Language = new DeeperData(language);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}\t\t{1}\t\t->{2}", Country, Capital, Language);
}
}
//Define the Prototype Interface and Handler Objects.
//Define the IPrototype abstract to be used as the base class for the main Prototype classes.
//The class defines the Clone() method (which does a shallow copy of the original object) and the DeepCopy() method.
//A shallow copy creates a new instance of the same type as the original object, and then copies the nonstatic fields of the original object; if the field is a value type, a bit-by-bit copy of the field is performed; If the field is a reference type, the reference is copied but the referred object is not; therefore, the reference in the original object and the reference in the clone point to the same object.
//In contrast, a deep copy of an object duplicates everything directly or indirectly referenced by the fields in the object.
[Serializable]
public abstract class IPrototype
{
public ProtoType Clone()
{
return (ProtoType) MemberwiseClone();
}
public ProtoType DeepCopy()
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
ProtoType copy = (ProtoType) formatter.Deserialize(stream);
stream.Close();
return (copy);
}
}
//The DeeperData class (object) is an extension to the Prototype class (object) and represents a referred object in the Prototype class (object).
[Serializable]
public class DeeperData
{
public string Data { get; set; }
public DeeperData(string s)
{
Data = s;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return (Data);
}
}
//The ProtoType class (object) represents the original prototype class, from which other classes will be cloned.
[Serializable]
public class ProtoType : IPrototype
{
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Capital { get; set; }
public DeeperData Language { get; set; }
public ProtoType(string country, string capital, string language)
{
Country = country;
Capital = capital;
Language = new DeeperData(language);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}\t\t{1}\t\t->{2}", Country, Capital, Language);
}
}
//Define the IPrototype abstract to be used as the base class for the main Prototype classes.
//The class defines the Clone() method (which does a shallow copy of the original object) and the DeepCopy() method.
//A shallow copy creates a new instance of the same type as the original object, and then copies the nonstatic fields of the original object; if the field is a value type, a bit-by-bit copy of the field is performed; If the field is a reference type, the reference is copied but the referred object is not; therefore, the reference in the original object and the reference in the clone point to the same object.
//In contrast, a deep copy of an object duplicates everything directly or indirectly referenced by the fields in the object.
[Serializable]
public abstract class IPrototype
{
public ProtoType Clone()
{
return (ProtoType) MemberwiseClone();
}
public ProtoType DeepCopy()
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
ProtoType copy = (ProtoType) formatter.Deserialize(stream);
stream.Close();
return (copy);
}
}
//The DeeperData class (object) is an extension to the Prototype class (object) and represents a referred object in the Prototype class (object).
[Serializable]
public class DeeperData
{
public string Data { get; set; }
public DeeperData(string s)
{
Data = s;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return (Data);
}
}
//The ProtoType class (object) represents the original prototype class, from which other classes will be cloned.
[Serializable]
public class ProtoType : IPrototype
{
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Capital { get; set; }
public DeeperData Language { get; set; }
public ProtoType(string country, string capital, string language)
{
Country = country;
Capital = capital;
Language = new DeeperData(language);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}\t\t{1}\t\t->{2}", Country, Capital, Language);
}
}